Have you ever wondered what makes your laser printer create those sharp, clear images and text every time? The secret lies in something called toner.
But what exactly is toner, and how does it work inside your printer to bring your documents to life? Understanding the science behind toner can help you appreciate the technology you use daily and even improve your printing results. Keep reading, because we’re about to reveal the fascinating process that turns tiny particles into perfect prints right before your eyes.
Toner Composition
Toner is a key material in laser printing. It creates the images and text on paper. Understanding its composition helps explain how laser printers work so well. Toner is not just ink. It is a fine powder made up of several parts. Each part plays a special role in printing quality and efficiency.
Components Of Toner
Toner mainly consists of tiny particles. These particles include pigments, polymers, and additives. Pigments give toner its color. Polymers bind the pigment and help it stick to paper. Additives improve the flow and charging of the powder. The size of toner particles is very small, usually under 10 microns. This size helps printers produce sharp and clear images.
Role Of Pigments And Polymers
Pigments provide the color needed for printing. Black toner uses carbon black pigment. Color toners use different pigments like cyan, magenta, and yellow. Polymers act as a binding agent. They melt during printing to fix the pigment on paper. This melting creates durable, smudge-resistant prints. The right mix of pigments and polymers ensures vibrant and lasting prints.

Credit: www.hp.com
Laser Printing Process
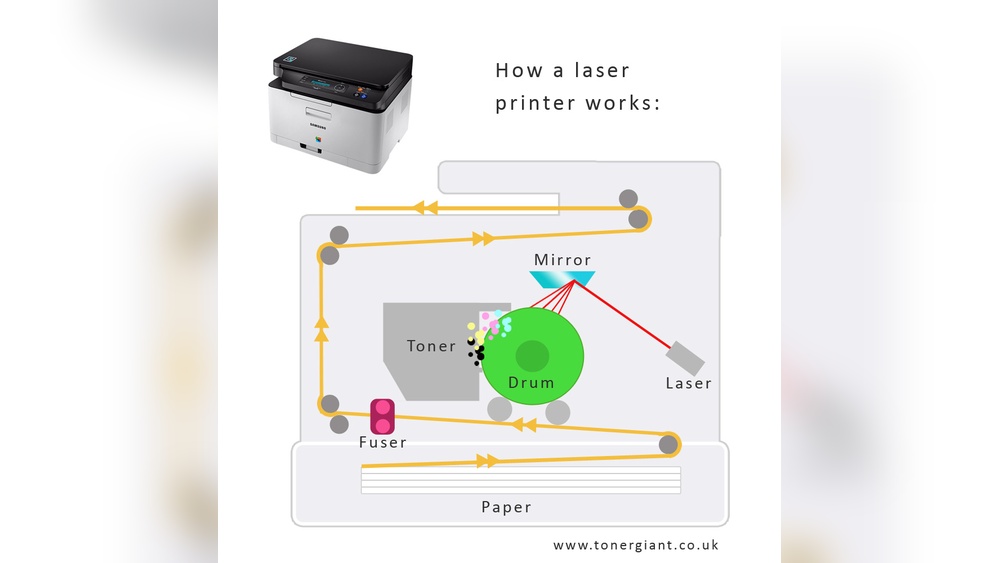
Toner in laser printers is a fine powder that sticks to paper using static electricity. A laser draws the image, and heat melts the toner to create clear prints. This process makes printing fast and sharp.
The laser printing process is a clever mix of light and static electricity. It creates sharp text and clear images on paper quickly and cleanly. This process uses a laser beam to build an image on a drum inside the printer.
The image forms with static electric charges, attracting toner particles to the paper. The toner then fuses to the paper with heat, making the print permanent.
Electrostatic Image Formation
A special drum inside the printer gets an electric charge. The laser beam shines on the drum in the shape of the image or text. The light changes the electric charge only in the places the laser hits.
This creates an invisible electrostatic image on the drum. The charged areas attract toner particles, while other areas do not.
Toner Attraction To The Image
The toner is a fine powder with a charge opposite to the drum’s charged areas. The toner sticks only to the charged parts of the drum. This process creates a visible image made of toner particles.
Next, the toner is transferred from the drum to paper. The paper also gets a charge to pull the toner off the drum. Finally, heat melts the toner onto the paper, making the print last.
Toner Fusion
Toner fusion is a key step in laser printing. It makes the printed image or text stick firmly to the paper. Without toner fusion, the toner powder would just rub off easily. This process uses heat and pressure to melt the toner particles. The melted toner bonds with the paper fibers. The result is a sharp, durable print that does not smudge or fade quickly.
Heat And Pressure Mechanism
Heat plays a vital role in toner fusion. The printer uses a fuser unit that heats up to a high temperature. This heat melts the toner powder on the paper. At the same time, pressure from rollers presses the paper. This pressure helps the melted toner spread evenly and stick well. The combination of heat and pressure ensures the toner becomes part of the paper surface. This is why laser prints feel smooth and stay intact.
Fusing The Toner To Paper
The toner is made of tiny plastic particles and color pigments. When heated, the plastic melts and flows into the paper’s surface. It fills tiny holes and fibers in the paper. As the paper cools, the toner solidifies and locks in place. This process prevents the toner from rubbing off or smearing. It also creates a clear and crisp image. Proper fusing is essential for good print quality and durability.
Toner Particle Technology
Toner particle technology is key to laser printer function. It controls print quality and efficiency. Toner particles are tiny powders that create images on paper. Their design affects how sharp and clear prints appear. Understanding these particles helps explain how laser printers work.
Particle Size And Shape
Toner particles are very small, often less than 10 microns wide. Small size allows smooth and detailed prints. The shape of particles varies from round to irregular. Round particles flow easily and create even layers. Irregular shapes help particles stick well to paper. Manufacturers balance size and shape for best results.
Charge Properties
Toner particles carry an electric charge. This charge controls where particles go on the drum. The laser changes the charge on the drum to form an image. Oppositely charged toner particles stick to these areas. Proper charge ensures clear and sharp printing. Charge properties also prevent particles from clumping together.
Common Toner Issues
Toner issues can affect print quality and slow down work. Understanding common problems helps fix them fast. Toner problems often show as marks or poor print on paper. These issues usually come from toner or printer parts. Knowing signs of toner trouble helps keep prints clear and sharp.
Toner Smudging
Toner smudging happens when toner powder does not stick well. It can smear on paper or hands after printing. Low fuser temperature or dirty rollers cause smudging. Using the wrong paper type also leads to smudges. Fixing smudging needs cleaning printer parts and checking settings.
Clumping And Streaking
Toner clumps form when powder sticks together inside the cartridge. Clumping causes dark spots or streaks on prints. Streaking appears as lines or gaps on the page. It often results from old or damp toner. Cleaning the drum and replacing toner can stop clumps and streaks.

Credit: www.brother.co.uk
Advancements In Toner Science
Toner science has seen many changes in recent years. These changes make laser printing better for users and the planet. New toner types help printers work more smoothly and produce clearer images. Technology improvements also reduce waste and lower energy use.
These advancements help printers use safer materials. They also improve color quality and sharpness. Each new step in toner science helps create more efficient and eco-friendly printing solutions. Let’s explore some key developments in this area.
Eco-friendly Toner Options
Many companies now make toner from natural and recycled materials. These toners use less plastic and harmful chemicals. They reduce pollution and help protect the environment. Some toners are designed to work with less energy during printing. This reduces the printer’s carbon footprint. Using eco-friendly toner supports greener office practices and lowers waste.
Improved Print Quality Techniques
New toner particles are smaller and more uniform. This change helps create sharper and clearer prints. Printers can now produce richer colors and finer details. Improved toner formulas also prevent smudging and fading. These changes ensure prints last longer and look better. Better print quality makes documents easier to read and more professional.

Credit: www.hp.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Toner In Laser Printers?
Toner is a fine powder used in laser printers to form text and images. It melts onto paper during printing, creating sharp, durable prints.
How Does Toner Work In Laser Printing?
Laser printers use static electricity to attract toner particles onto a drum. The toner is then fused to paper with heat and pressure, producing prints.
Why Is Toner Preferred Over Ink In Laser Printers?
Toner produces faster, smudge-resistant prints with higher durability. It also handles large print volumes efficiently and offers crisp image quality compared to ink.
Can Toner Cartridges Be Refilled Or Reused?
Yes, toner cartridges can be refilled or remanufactured. This saves cost and reduces waste, but quality depends on the refilling process and toner used.
Conclusion
Toner plays a vital role in laser printing. It sticks to the paper using heat and static electricity. This process creates sharp, clear images and text. Understanding toner helps you appreciate how laser printers work. It also explains why toner quality matters for good prints.
Knowing this science can help you choose the right printer supplies. Clear prints depend on toner and printer working well together. Simple, yet powerful technology behind every printed page.
Affiliate Disclosure
This website/blog/content contains affiliate links. This means if you click on one of these links and make a purchase, I may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you.
I only recommend products and services that I genuinely believe in and have personally used or thoroughly researched. While I do receive compensation for these recommendations, my opinions remain honest and unbiased.
The commissions earned help support this website and allow me to continue providing valuable content. I appreciate your support when you use these links, but you are never obligated to make purchases through them.
Please note that prices of products or services may vary, and I have no control over these prices or the availability of items. All recommendations are made based on my assessment at the time of posting.
Thank you for your understanding and support.